In some eukaryotic genes there are regions that help increase or enhance transcription. Hence transcription produces a monocistronic mRNA.
Overview Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Article Khan Academy
Describe how most eukaryotic genes are controlled What are the key molecular components and genetic elements needed for gene expression transcription in bacteria.
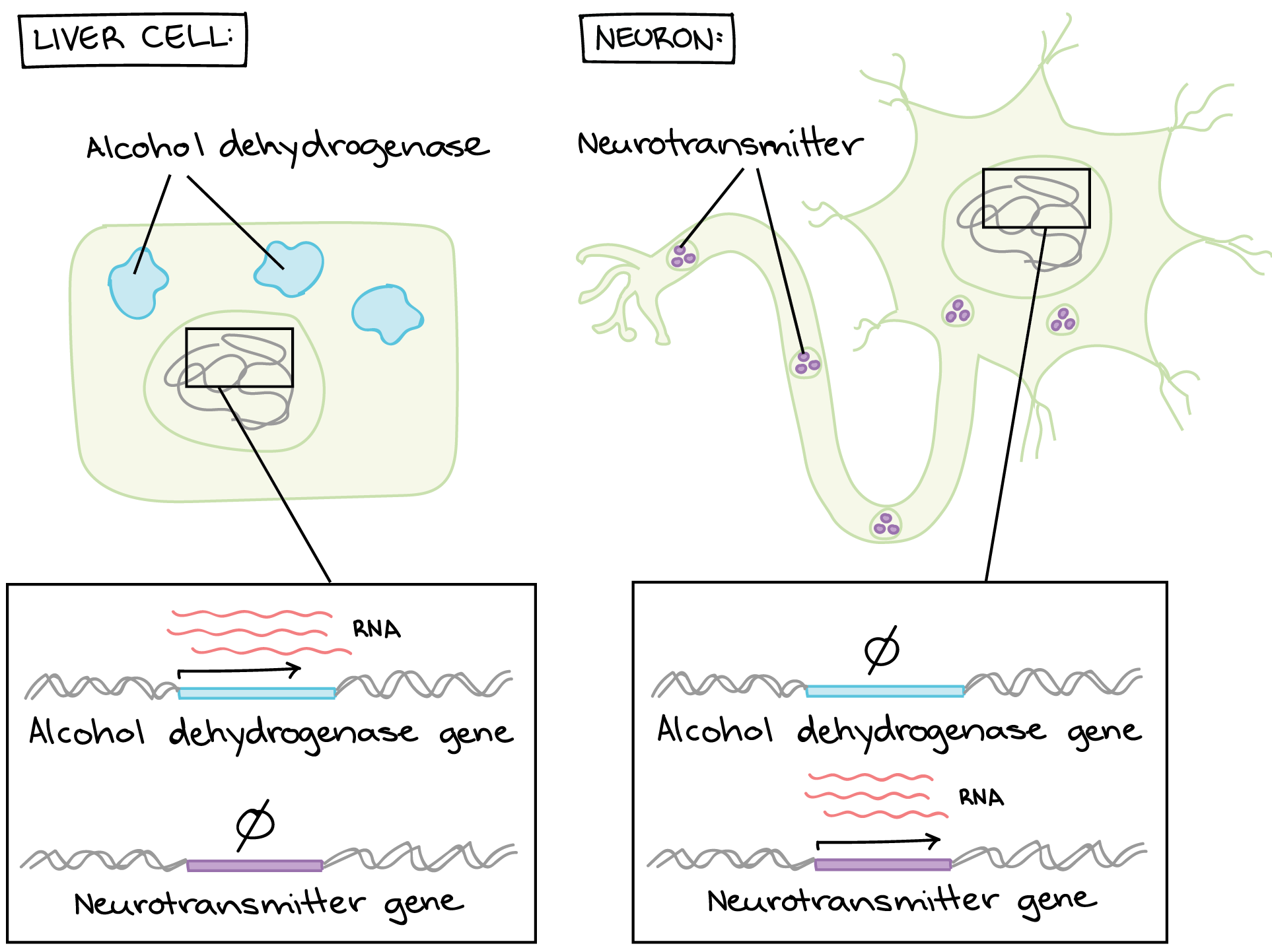
. RNA polymerase II is responsible for transcribing the overwhelming majority of eukaryotic genes including all of the protein-encoding genes which ultimately are translated into proteins and genes for several types of regulatory RNAs including microRNAs miRNAs and long-coding RNAs lncRNAs. Describe how most eukaryotic genes are controlled. In this way the protein tightly condenses the part of DNA which is not planed to be used.
Histone has a job. Gene expression is primarily controlled at the level of transcription largely as a result of binding of proteins to specific sites on DNA. The gene control in eukaryotic cells particularly during differentiation is one of the most extensively studied areas in biology with special reference to molecular mechanism.
The latest estimates are that a human cell a eukaryotic cell contains some 21000 genes. The regions between genes are likewise not expressed but may help with chromatin assembly contain promoters and so forth. Coordinate gene expression in eukaryotes depends on.
Sets of transcription factor proteins bind to. In addition eukaryotic cells have many more genes than prokaryotic cells. Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes.
Control of Gene Expression. Genes that are expressed usually have introns that interrupt the coding sequences. Complex gene regulation in eukaryotes makes cell specialization possible.
Most eukaryotic cells are controlled individually and have a much more complex regulatory system than those of the lac repressor system. These mechanisms control how DNA is packed into the nucleus by regulating how tightly the DNA is wound around histone proteins. In addition coordinately controlled genes in eukaryotic cells are activated by the same chemical signals.
Most eukaryotic genes are controlled individually and have regulatory sequences that are much more complex than those of the lac operon. Many plasmids have been recognized for E. Respiration common to all cells.
Describe how most eukaryotic genes are controlled. More commonly genes coding for the enzymes of a metabolic pathway are scattered over different chromosomes. Recall that in eukaryotic cells the DNA is contained inside the cells nucleus and that is where it is transcribed to produce mRNA.
The F plasmid contains 25 genes some of which control the production of F pili proteins which extend from the surface of F or male cells to the surface of F - or female cells. Genes are regulated in eukaryotes through transcription factorsand enhancer sequences. The coordinate regulation of clustered genes in eukaryotic cells is thought to involve changes in the chromatin structure that makes the entire group of genes either available or unavailable for transcription.
Eukaryotic genes are not organized into operons so each gene must be regulated independently. Epigenetic mechanisms control access to the chromosomal region to allow genes to be turned on or off. The particular combination of genes for a given trait in a given organism.
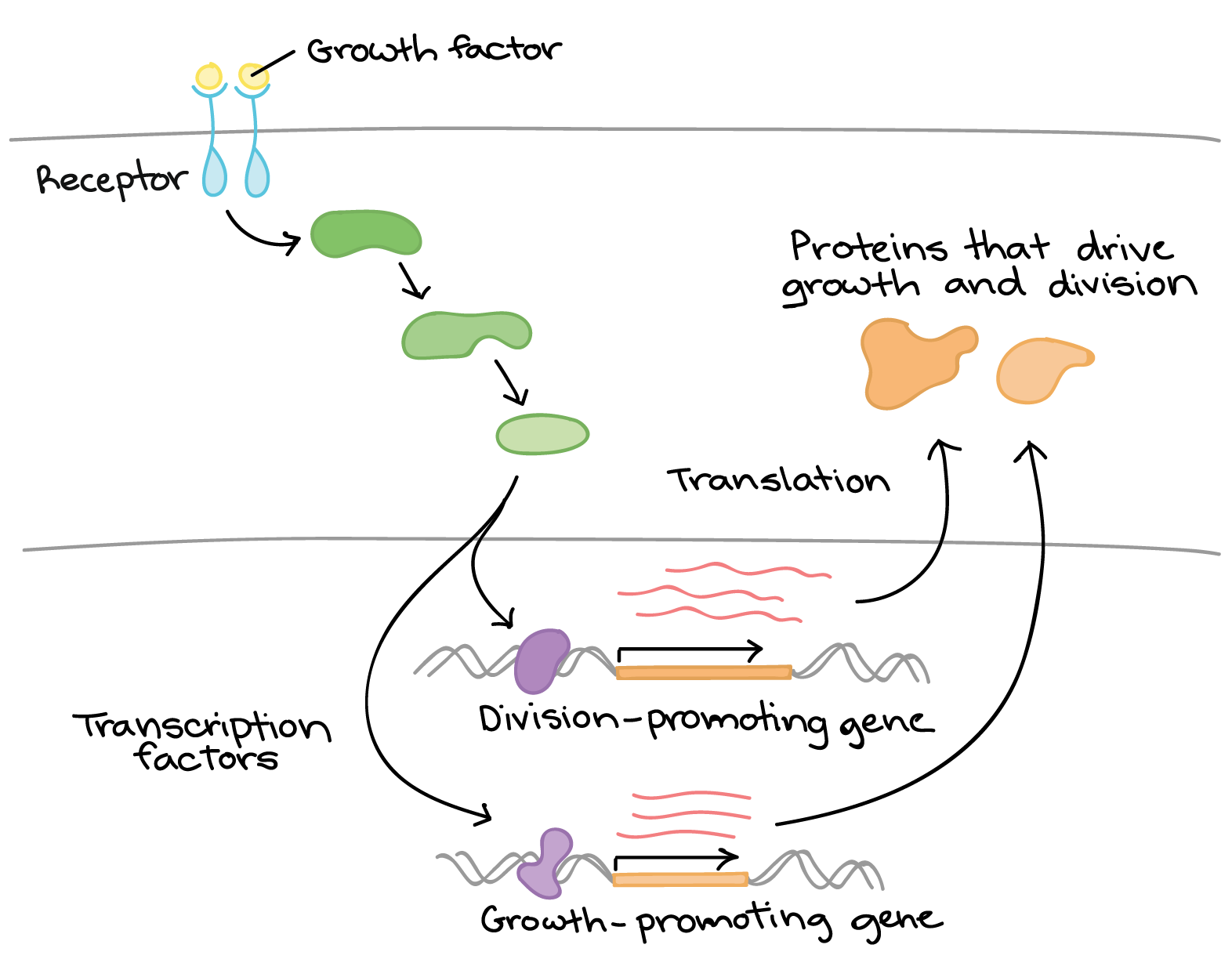
Some of these are expressed in all cells all the time. Transcription is a key regulatory point for many genes. Transcription factors are proteins thatbind to the DNA and in turn help RNA polymerase.
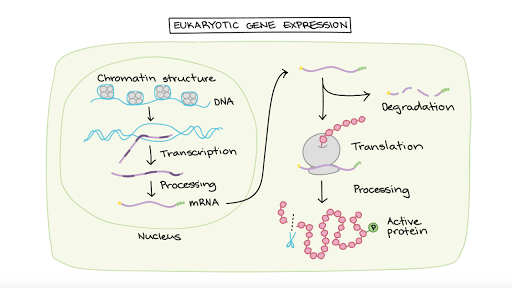
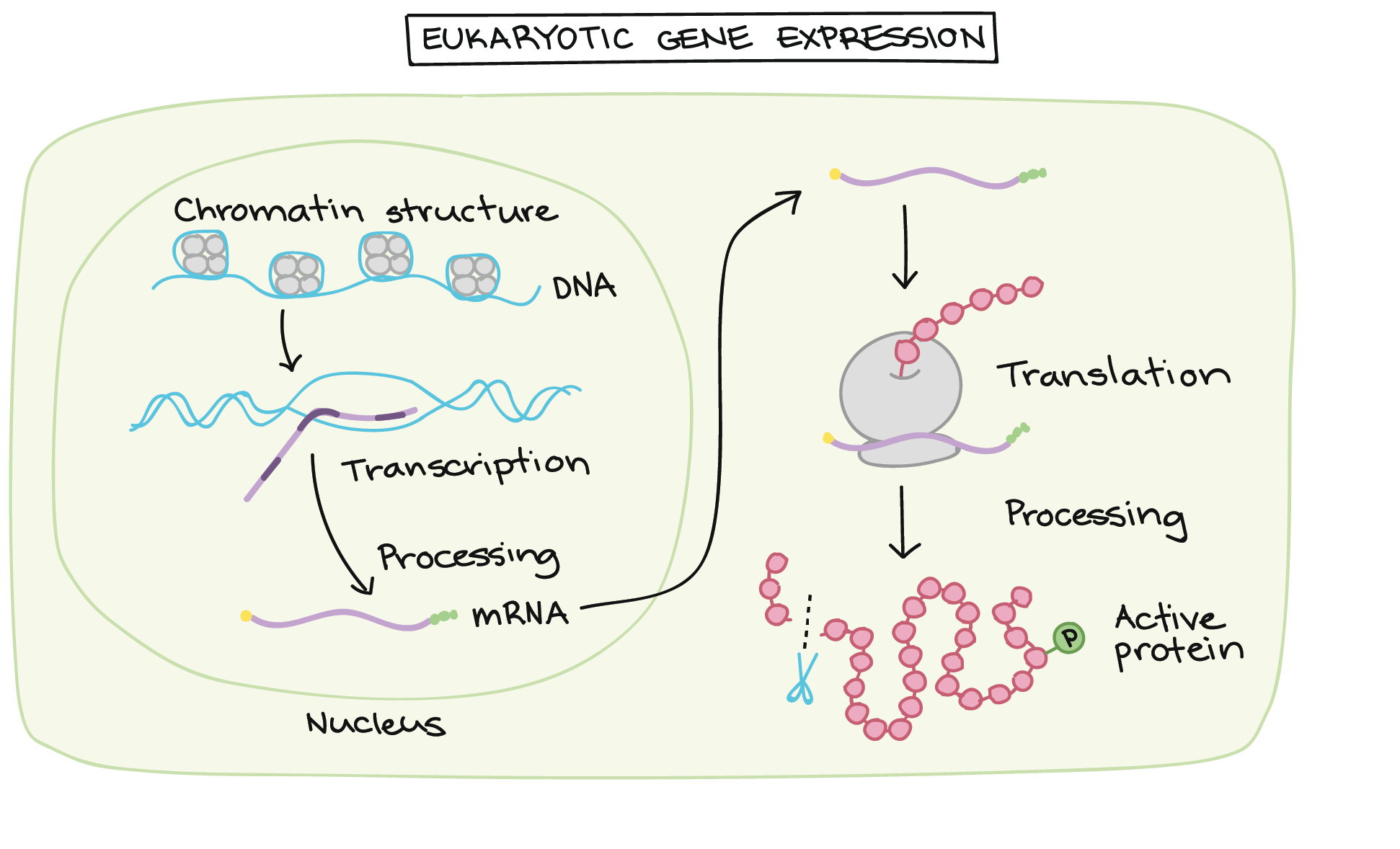
Control of transcriptional initiation is a primary means used to regulate gene expression in eukaryotic organisms. You just studied 5 terms. It makes packaging by binding DNA and wounding it.
Alternative RNA Splicing In the 1970s genes were first observed that exhibited alternative RNA splicing. RNA polymerase III is also located in the nucleus. The structure of chromatin DNA and its organizing proteins can be regulated.
The genes control the synthesis of various proteins in various cells. Eukaryotic gene expression can be regulated at many stages Chromatin accessibility. In eukaryotic cells the first stage of gene expression control occurs at the epigenetic level.
In 1965 Francois Jacob Jacques Monod and Andre Lwoff shared the Nobel prize in. Therefore in prokaryotic cells the control of gene expression is almost entirely at the transcriptional level. Alternative RNA splicing is a mechanism that allows different protein products to be produced from one gene when different combinations of exons are combined to form the mRNA This alternative splicing can be haphazard but more often it is controlled and acts as a.
Most eukaryotic genes are controlled at the level of transcription by proteins trans-acting factors that interact with specific gene sequences cis. Regulation of gene expression can happen at any of the stages as DNA is transcribed into mRNA and mRNA is translated into protein. Gene promoters have multiple binding sites for transcription factors each of which can influence transcription.
By gene expression we mean the transcription of a gene into mRNA and its subsequent translation into protein. A typical eukaryotic gene therefore consists of a set of sequences that appear in mature mRNA called exons interrupted by introns. It gives specific transcription factors bind to control elements promoting transcription of coordinately controlled genes even if the genes are on separate chromosomes.
Control the expression of genes in eukaryotes by binding DNA sequences in the regulatory regions. By enzymes and proteins For example gene expression is controlled in eukaryotes by the protein called Histone. Coli including the F plasmids sex factors and R plasmids drugantibiotic resistance.
These so-called housekeeping genes are responsible for the routine metabolic functions eg. In contrast a eukaryotic gene can be vastly more complex and can occupy large regions of chromosomes. The lac genes are turned off by repressors and turned on by the presence of lactose.
Eukaryotic cells in contrast have intracellular organelles and are much more complex. CONTROL OF EUKARYOTIC GENOME. Its most significant difference is the presence of the TATA box which helps bind a protein to position RNA polymerase marking the point where a gene begins.
Overview Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Article Khan Academy
0 Comments